Section outline
-
Infrastructure of Quality - schematic representation (for Croatia)

-
Quality Control represent a set of activities for ensuring quality - from raw material to finish products, which were oriented on identifying defects in finished products or during the production process for corrective measures - using 7 QC tools and 8D probelm - solving methodology.
We said that the QC is a reactive approach.
-
-
Examples of good practice of Multiple Linear Regression and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models which were used for for predicting the thermal protective and thermo-physiological comfort performances. Through a comparison of the predicting performance parameters of these models, it has been found that ANN models can more accurately predict the performances of fabrics.
These models can be implemented in the textile industry and academia for effectively and conveniently predicting the thermal protective and thermo-physiological comfort performances only by utilizing the key fabric properties.
-
-
The technological process of garment finishing is the final and very important part of the garment manufacturing process in which garments get their final appearance.
The final appearance of clothing, its fit to the human body and the presentation to the buyers all have a significant effect on sales.
The technological finishing process requires the use of high quality machines and equipment to correct any minor defects that appear during the process of clothing manufacturing to ensure the garment fits the 3D body shape and to prepare the final product for packaging.
Quality control and quality assurance are complex areas in the apparel industry and in this part will be explained on final inspection of Men's jacket.
3.2 MB -
Some od Quality Definitions
 1.5 MB
1.5 MB -
-
-
Requirements to Implement a QMS
All quality management systems must address a company’s unique set of needs; however, we can name a few general elements that all QMS have in common, such as:
- The creation of a quality manual.
- The existence of quality objectives and policies.
- A set of procedures, records, and instructions about all internal processes, data management, quality analysis, improvement opportunities, and customer satisfaction.
Each aspect of a QMS is intended to serve a specific purpose that in the end will help to achieve the final goal: meeting both the organization’s and customer’s needs.
TQM enables organizations to align their workforce with the manufacturing processes to find and eliminate errors to improve the overall quality of their outputs.
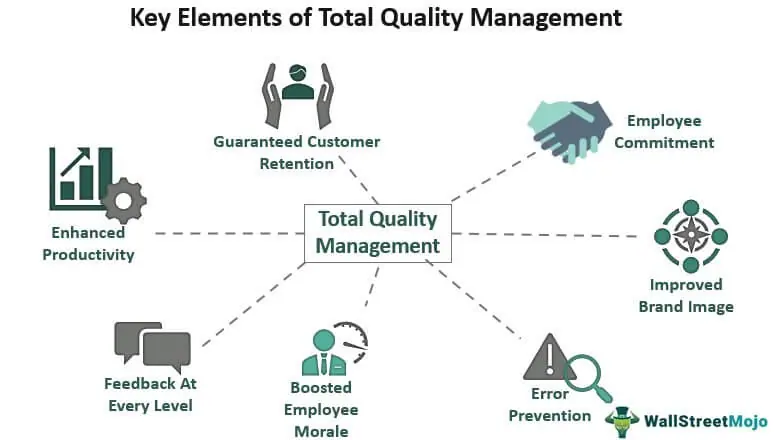
Fig.: Key elements in TQM
Source: Total Quality Management (TQM) - Principles, Elements, Examples (wallstreetmojo.com)
It is very important to know does the final product is higher than the market standards, legal requirements, and customer expectations!
1.3 MB -
Here you can find a paper with included a case study of selected models of quality management implemented at a private university in Slovakia, especially the process model ISO 9001 and the common assessment framework (CAF) model, with the advantages and disadvantages resulting from the implementation of quality management models.
Source: Girmanová, L.; Šolc, M.; Blaško, P.; Petrík, J. Quality Management System in Education: Application of Quality Management Models in Educational
Organization—Case Study from the Slovak Republic. Standards 2022, 2,460–473. https://doi.org/10.3390/standards2040031
-
Certification Process
1. Preliminary audit (optional):
This is initial assessment of the QMS implementation in company, and the audit focuses mainly on the areas of the system for which further improvements according to ISO requirements are needed. After identification and eradicating potential vulnerabilities in the management system, the audit in relation to the certification begins.
2. Certification audit:
This phase is comprised of a stage 1 and stage 2 audit consists of detailed review where, the auditors assess documentation and practical application of quality management system according to certification requirements.
3. Issue Certificate:
Once when the auditors who are experts in the sector, identifies that audited QMS satisfies the requirements of ISO 9001:2015, accredited certification body with expertise in QMS will Issue the ISO 9001:2015. certificate.
4. Surveillance audit:
Annual surveillance of the processes optimization in company and quality management system to ensure conformity of the system with the ISO standards carried out.
5. Re-certification:
Every 3 years from the certificate date, which is also maximum validity of the certificate, organization passes the re-certification process for the next term.
Source: ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System Certification in UK| dubai| oman| qatar| bahrain (traibcert.org.uk)
1.1 MB -
Quality assurance and quality control represents a two elements of quality management.
Even are quality assurance and quality control activities are linked, still they are defined differently. Typically, QA activities and responsibilities cover virtually all of the quality system, while QC is a subset of the QA activities.
Sometimes, elements in the quality system might not be specifically covered by QA/QC activities and responsibilities but again may involve QA and QC.
Fig.: Quality system, Quality Assurance and Quality Control Relationship; Source: Quality Assurance vs Quality Control: Definitions & Differences | ASQ
-
Expected benefits of EMS
- More rational spending of natural resources and energy
- Reducing of the amount of waste and emissions
- Using renewable natural raw material and energy resources
General Benefits:- Increasing the efficiency and competitiveness of company
- Developing employees' awareness of the need for environmental protection.
1.4 MB -
The EU Eco-Management and Audit Scheme (EMAS) is a premium management instrument developed by the European Commission for companies and other organisations to evaluate, report, and improve their environmental performance.
EMAS is open to every type of organisation eager to improve its environmental performance. It spans all economic and service sectors and is applicable worldwide.
With EMAS, your organisation can reduce its environmental impacts, strengthen legal compliance and employee involvement, and save resources and money!
Click https://ec.europa.eu/environment/emas/index_en.htm link to open resource.
1.2 MB -
215.2 KB · Uploaded 31/01/22, 02:45
-
the European Commission has finally published the long-awaited EU strategy for sustainable and circular textiles.
-
👉 Looking for Ecological Footprint by Country 2022

-
-
-

